vfa_t1: Compute a T1 map using Variable Flip Angle¶
Contents
- 1. Print vfa_t1 information
- 2. Setting model parameters
- 2.a. Create vfa_t1 object
- 2.b. Set protocol and options
- 2.b.1 Set protocol the CLI way
- 2.b.2 Set protocol and options the GUI way
- 3. Fit MRI data
- 3.a. Load input data
- 3.b. Execute fitting process
- 3.c. Display FitResults
- 3.d. Save fit results
- 3.e. Re-use or share fit configuration files
- 4. Simulations
- 4.a. Single Voxel Curve
- 4.b. Sensitivity Analysis
- 5. Notes
- 5.a. Notes specific to vfa_t1
- 5.a.1 BIDS
- 5.b. Generic notes
- 5.b.1. Batch friendly option and protocol conventions
- 5.b.2 Parallelization:
- 6. Citations
% This m-file has been automatically generated using qMRgenBatch(vfa_t1) % for publishing documentation. % Command Line Interface (CLI) is well-suited for automatization % purposes and Octave. % % Please execute this m-file section by section to get familiar with batch % processing for vfa_t1 on CLI. % % Demo files are downloaded into vfa_t1_data folder. % % Written by: Agah Karakuzu, 2017 % ==============================================================================
1. Print vfa_t1 information
qMRinfo('vfa_t1');
Contents of vfa_t1:
vfa_blochsim - IR_BLOCHSIM Bloch simulations of the GRE-IR pulse sequence.
vfa_equation - S Analytical equations for the longitudinal magnetization of
vfa_t1 is both a directory and a function.
vfa_t1: Compute a T1 map using Variable Flip Angle
Assumptions:
Inputs:
VFAData Spoiled Gradient echo data, 4D volume with different flip angles in time dimension
(B1map) Normalized transmit excitation field map (B1+). B1+ is defined
as a normalized multiplicative factor such that:
FA_actual = B1+ * FA_nominal. (OPTIONAL).
(Mask) Binary mask to accelerate the fitting. (OPTIONAL)
Outputs:
T1 Longitudinal relaxation time [s]
M0 Equilibrium magnetization
Protocol:
VFAData Array [nbFA x 2]:
[FA1 TR1; FA2 TR2;...] flip angle [degrees] TR [s]
Options:
None
Example of command line usage:
Model = vfa_t1; % Create class from model
Model.Prot.VFAData.Mat=[3 0.015; 20 0.015]; %Protocol: 2 different FAs
data = struct; % Create data structure
data.VFAData = load_nii_data('VFAData.nii.gz');
data.B1map = load_nii_data('B1map.nii.gz');
FitResults = FitData(data,Model); %fit data
FitResultsSave_mat(FitResults);
For more examples: qMRusage(vfa_t1)
Author: Ian Gagnon, 2017
References:
Please cite the following if you use this module:
Fram, E.K., Herfkens, R.J., Johnson, G.A., Glover, G.H., Karis, J.P.,
Shimakawa, A., Perkins, T.G., Pelc, N.J., 1987. Rapid calculation of
T1 using variable flip angle gradient refocused imaging. Magn. Reson.
Imaging 5, 201?208
In addition to citing the package:
Karakuzu A., Boudreau M., Duval T.,Boshkovski T., Leppert I.R., Cabana J.F.,
Gagnon I., Beliveau P., Pike G.B., Cohen-Adad J., Stikov N. (2020), qMRLab:
Quantitative MRI analysis, under one umbrella doi: 10.21105/joss.02343
Reference page in Doc Center
doc vfa_t1
2. Setting model parameters
2.a. Create vfa_t1 object
Model = vfa_t1;
2.b. Set protocol and options
Protocol: MRI acquisition parameters that are accounted for by the respective model.
For example: TE, TR, FA FieldStrength. The assigned protocol values are subjected to a sanity check to ensure that they are in agreement with the data attributes.
Options: Fitting preferences that are left at user's discretion.
For example: linear fit, exponential fit, drop first echo.
2.b.1 Set protocol the CLI way
If you are using Octave, or would like to serialize your operations any without GUI involvement, you can assign protocol directly in CLI:
FlipAngle = [3.0000; 20.0000]; % FlipAngle is a vector of [2X1] TR = [0.0150; 0.0150]; % TR is a vector of [2X1] Model.Prot.VFAData.Mat = [ FlipAngle TR];
See the generic notes section below for further information.
2.b.2 Set protocol and options the GUI way
The following command opens a panel to set protocol and options (if GUI is available to the user):
Model = Custom_OptionsGUI(Model);
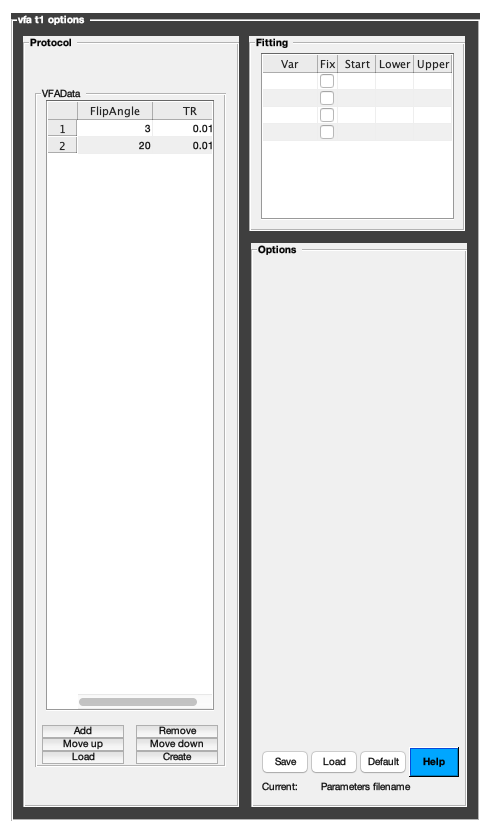
If available, you need to close this panel for the remaining of the script to proceed.
Using this panel, you can save qMRLab protocol files that can be used in both interfaces. See the generic notes section below for details.
3. Fit MRI data
3.a. Load input data
This section shows how you can load data into a(n) vfa_t1 object.
- At the CLI level, qMRLab accepts structs containing (double) data in the fields named in accordance with a qMRLab model.
See the generic notes section below for BIDS compatible wrappers and scalable
qMRLab workflows.
% |- vfa_t1 object needs 3 data input(s) to be assigned: % |- VFAData % |- B1map % |- Mask data = struct(); % VFAData.nii.gz contains [128 128 1 2] data. data.VFAData=double(load_nii_data('vfa_t1_data/VFAData.nii.gz')); % B1map.nii.gz contains [128 128] data. data.B1map=double(load_nii_data('vfa_t1_data/B1map.nii.gz')); % Mask.nii.gz contains [128 128] data. data.Mask=double(load_nii_data('vfa_t1_data/Mask.nii.gz'));
3.b. Execute fitting process
This section will fit the loaded data.
FitResults = FitData(data,Model,0);
Visit the generic notes section below for instructions to accelerate fitting by
parallelization using ParFitData.
3.c. Display FitResults
You can display the current outputs by:
qMRshowOutput(FitResults,data,Model);
A representative fit curve will be plotted if available.
To render images in this page, we will load the fit results that had been saved before. You can skip the following code block;
% Load FitResults that comes with the example dataset. FitResults_old = load('FitResults/FitResults.mat'); qMRshowOutput(FitResults_old,data,Model);
M0: 2.5567e+03
Model: [1x1 struct]
Protocol: [1x1 struct]
T1: 1.3447
Time: 0.0087
Version: [2 0 8]
computed: [128x128 double]
fields: {'T1' 'M0'}


3.d. Save fit results
Outputs can be saved as *.nii.(gz) if NIfTI inputs are available:
% Generic function call to save nifti outputs FitResultsSave_nii(FitResults, 'reference/nifti/file.nii.(gz)');
If not, FitResults.mat file can be saved. This file contains all the outputs as workspace variables:
% Generic function call to save FitResults.mat
FitResultsSave_mat(FitResults);
FitResults.mat files can be loaded to qMRLab GUI for visualization and ROI
analyses.
The section below will be dynamically generated in accordance with the example data format (mat or nii). You can substitute FitResults_old with FitResults if you executed the fitting using example dataset for this model in section 3.b..
FitResultsSave_nii(FitResults_old, 'vfa_t1_data/VFAData.nii.gz');
3.e. Re-use or share fit configuration files
qMRLab's fit configuration files (vfa_t1_Demo.qmrlab.mat) store all the options and protocol in relation to the used model and the release version.
*.qmrlab.mat files can be easily shared with collaborators to allow them fit their own
data or run simulations using identical option and protocol configurations.
Model.saveObj('my_vfa_t1_config.qmrlab.mat');
4. Simulations
4.a. Single Voxel Curve
Simulates single voxel curves
Not available for the current model.
4.b. Sensitivity Analysis
Simulates sensitivity to fitted parameters
Not available for the current model.
5. Notes
5.a. Notes specific to vfa_t1
5.a.1 BIDS

|== sub-01/ |~~~~~~ anat/ |---------- sub-01_flip-1_VFA.json |---------- sub-01_flip-1_VFA.nii.gz |---------- sub-01_flip-2_VFA.json |---------- sub-01_flip-2_VFA.nii.gz |---------- . |---------- . |---------- sub-01_flip-N_VFA.json |---------- sub-01_flip-N_VFA.nii.gz | |== derivatives/ |~~~~~~ qMRLab/ |---------- dataset_description.json |~~~~~~~~~~ sub-01/anat/ |-------------- sub-01_T1map.nii.gz |-------------- sub-01_T1map.json |-------------- sub-01_R1map.nii.gz |-------------- sub-01_R1map.json |-------------- sub-01_M0map.nii.gz |-------------- sub-01_M0map.json
For further information, please visit BIDS qMRI Appendix.
5.b. Generic notes
5.b.1. Batch friendly option and protocol conventions
If you would like to load a desired set of options / protocols programatically, you can use *.qmrlab.mat files. To save a configuration from the protocol panel of vfa_t1, first open the respective panel by running the following command in your MATLAB command window (MATLAB only):
Custom_OptionsGUI(vfa_t1);
In this panel, you can arrange available options and protocols according to your needs, then click the save button to save my_vfa_t1.qmrlab.mat file. This file can be later loaded into a vfa_t1 object in batch by:
Model = vfa_t1;
Model = Model.loadObj('my_vfa_t1.qmrlab.mat');
Model.loadObj('my_vfa_t1.qmrlab.mat') call won't update the fields in the Model object, unless the output is assigned to the object as shown above. This compromise on convenience is to retain Octave CLI compatibility.
If you don't have MATLAB, hence cannot access the GUI, two alternatives are available to populate options:
- Use qmrlab/mcrgui:latest Docker image to access GUI. The instructions are available here.
- Set options and protocols in CLI:
- List available option fields using tab completion in Octave's command prompt (or window)
Model = vfa_t1;
Model.option. % click the tab button on your keyboard and list the available fields.
- Assign the desired field. For example, for a mono_t2 object:
Model = mono_t2; Model.options.DropFirstEcho = true; Model.options.OffsetTerm = false;
Some option fields may be mutually exclusive or interdependent. Such cases are handled by the GUI options panel; however, not exposed to the CLI. Therefore, manual CLI options assignments may be challenging for some involved methods such as qmt_spgr or qsm_sb. If above options are not working for you and you cannot infer how to set options solely in batch, please feel free to open an issue in qMRLab and request the protocol file you need.
Similarly, in CLI, you can inspect and assign the protocols:
Model = vfa_t1;
Model.Prot. % click the tab button on your keyboard and list the available fields.
Each protocol field has two subfields of Format and Mat. The first one is a cell indicating the name of the protocol parameter (such as EchoTime (ms)) and the latter one contains the respective values (such as 30 x 1 double array containing EchoTimes).
The default Mat protocol values are set according to the example datasets served via OSF.
5.b.2 Parallelization:
The current model does not perform voxelwise fitting. Therefore, parallelization is not enabled.
6. Citations
qMRLab JOSS article
Karakuzu A., Boudreau M., Duval T.,Boshkovski T., Leppert I.R., Cabana J.F., Gagnon I., Beliveau P., Pike G.B., Cohen-Adad J., Stikov N. (2020), qMRLab: Quantitative MRI analysis, under one umbrella 10.21105/joss.02343
Reference article for vfa_t1
Quantitative MRI, under one umbrella.
NeuroPoly Lab, Montreal, Canada